Automating Dependency Updates
Over the years, I’ve been involved with various software development projects. Once an application shifts into production, maintenance becomes essential—not just fixing bugs or shipping features, but ensuring the software remains secure, performant, and compatible with its evolving ecosystem.
One key aspect of maintenance is ensuring dependencies remain up-to-date. Outdated dependencies can miss bug fixes and improvements, and introduce security vulnerabilities. However, as applications grow or additional applications need support, the task of manually tracking and updating dependencies can become increasingly error-prone and time-consuming.
Automating dependency updates is therefore key to ensuring bug fixes, improvements, and security fixes are applied swiftly, while limiting the growth of manual involvement from developers. In this post, I’ll share how I set up Dependabot initially, before later adopting Renovate to handle my automation of updates.
Getting Started with Dependabot
GitHub is one of the largest and most popular source code platforms and comes with built-in support for automated dependency updates via Dependabot. Dependabot has support for numerous package ecosystems and works by scanning repositories for dependency updates, raising pull requests (PR) when updates are found.
Dependabot has two main features:
- Security Updates – Scanning and proposing updates for vulnerable dependencies
- Version Updates – General purpose dependency updates
Let’s start by looking at security updates.
Dependabot Security Updates
As mentioned, the security updates feature scans for vulnerable dependencies and raises PRs updating dependencies to a secure version.
You can enable the security updates feature in the Settings of a repository. In Security > Advanced Security, you’ll find the Dependabot section.
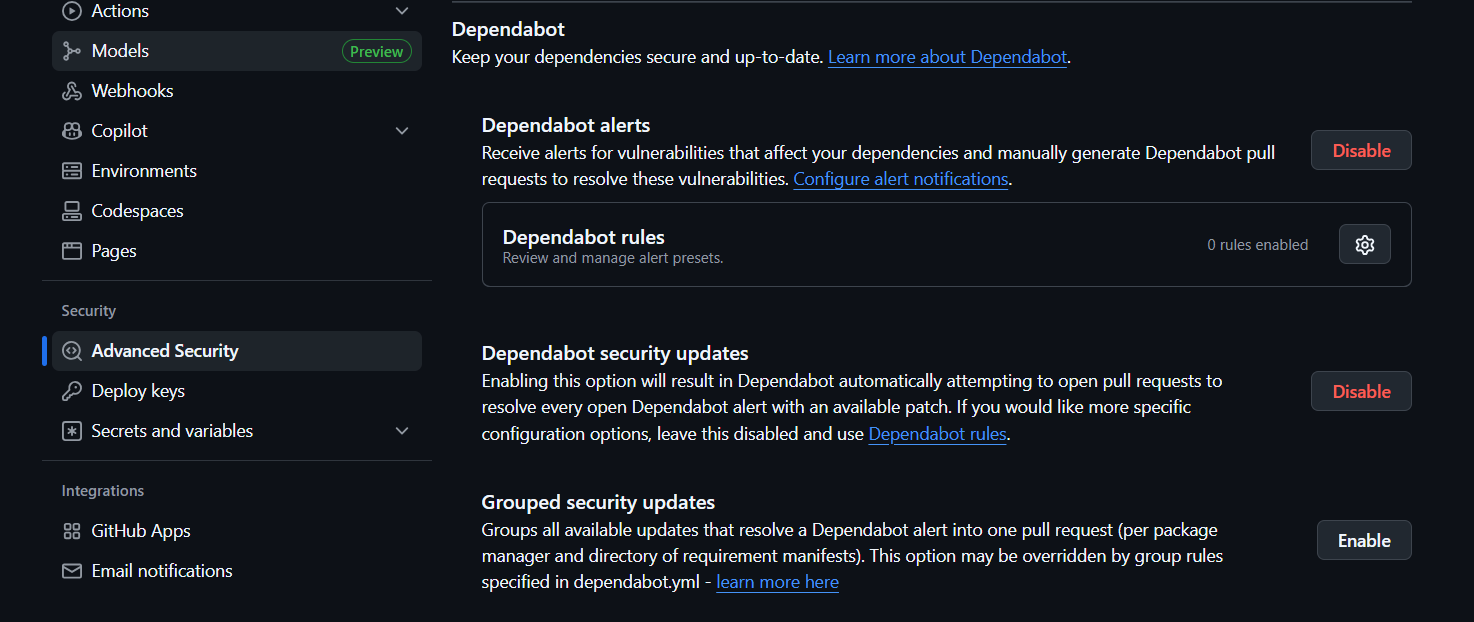
Enabling either Dependabot security updates or Grouped security updates will enable scanning the repo.
Any vulnerabilities that are found will be listed in the Security > Dependabot area of the repository, along with severity details and a brief description.
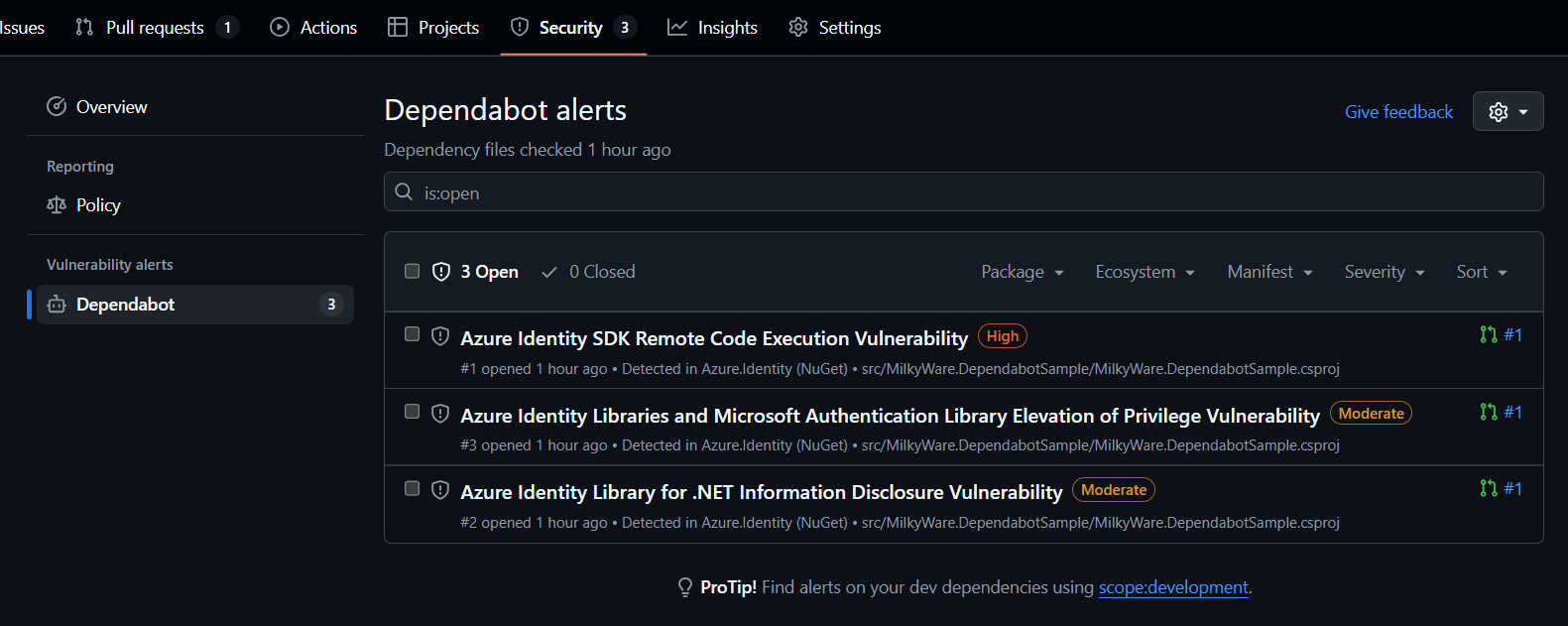
Notice that on the far right of these alerts is a reference to the same PR, #1. In this case, all of the alerts are addressed by the same PR. We can then review the details of the PR and merge it.
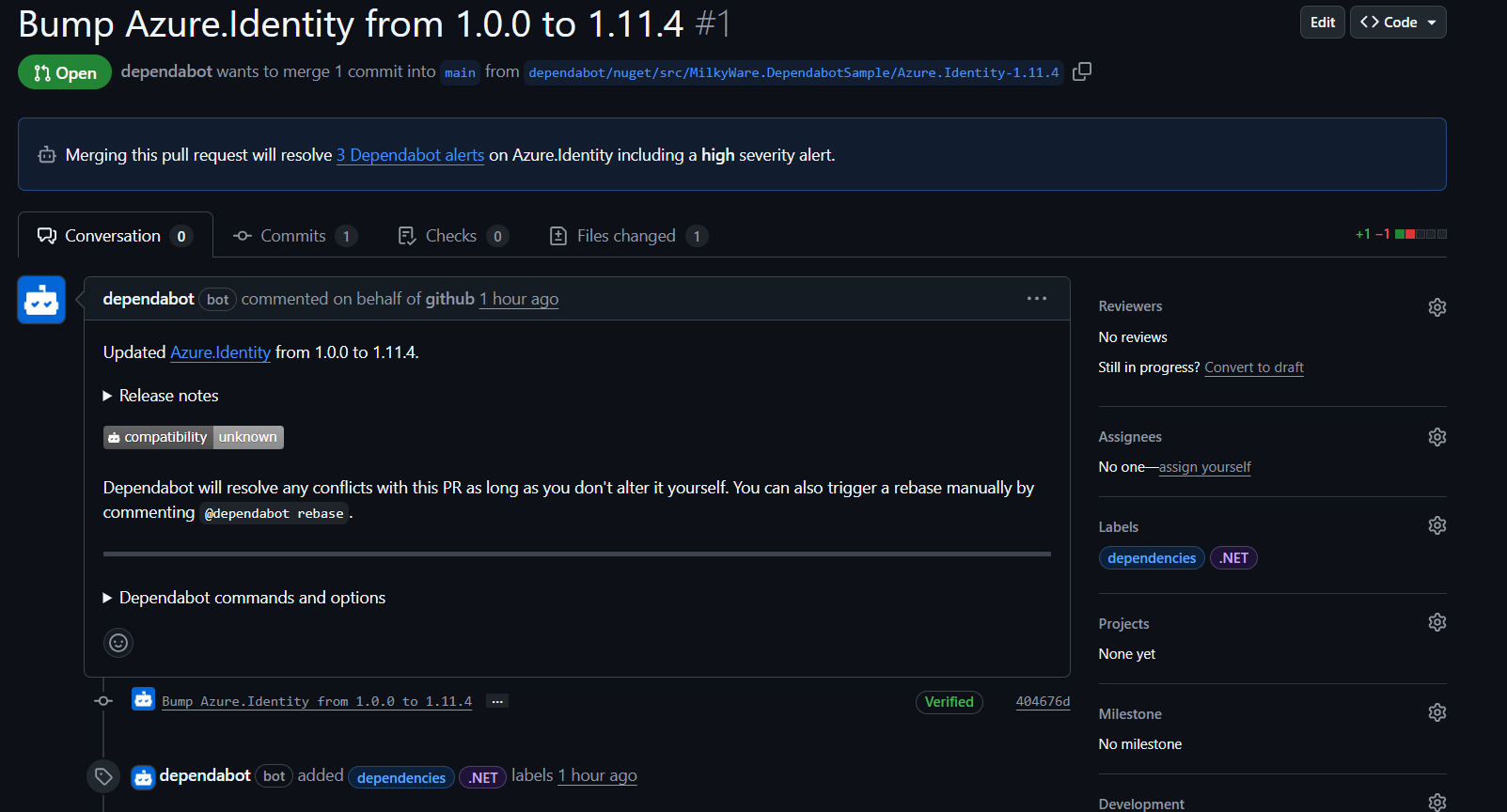
These PRs are subject to the same checks the repository has configured, such as peer reviews and automated CI builds, to ensure the code continues to work.
Enabling by Default
GitHub also offers the ability to enable this feature by default and configure it en masse for all repositories, either for a user or an organisation. This can be found in Settings > Code Security > Dependabot under the same two settings as in the repository: Dependabot security updates and Grouped security updates.
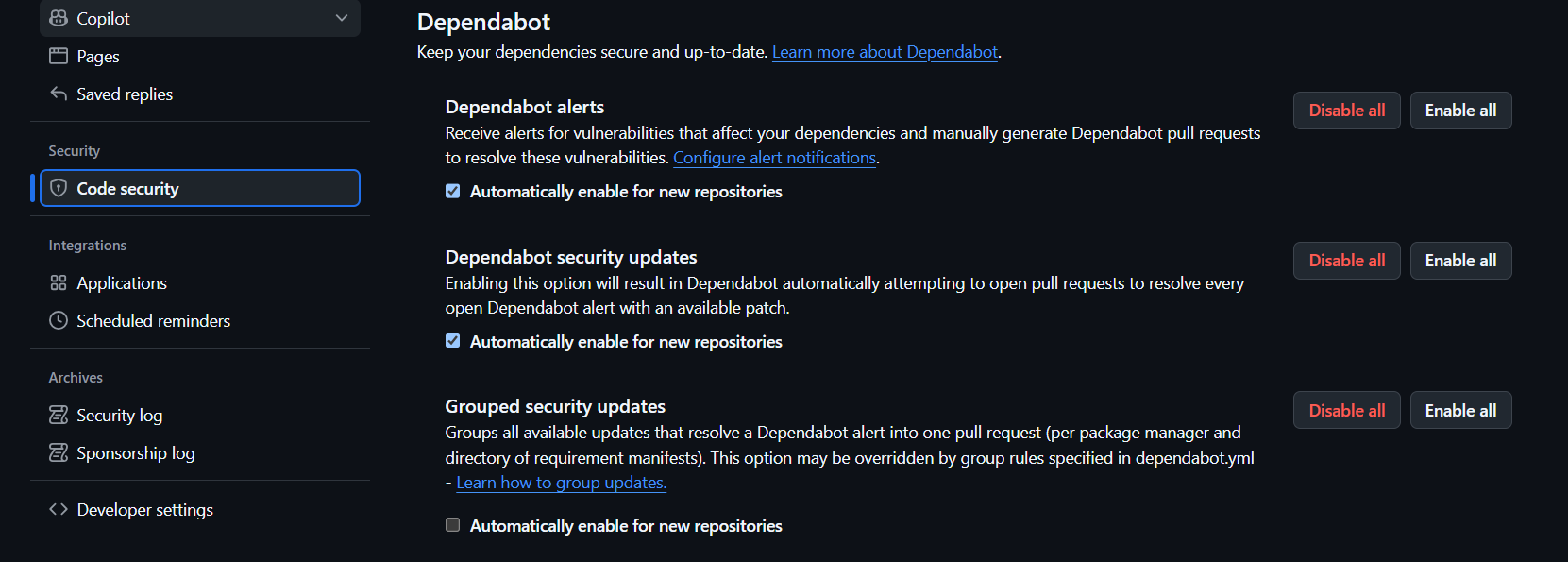
Enabling this feature by default will help ensure that all your future projects remain secure with no additional setup effort required.
Configuring Version Updates
While security updates are triggered by the discovery of vulnerabilities, version updates allow you to keep all your dependencies up-to-date as soon as new versions are released. With version updates enabled, Dependabot will automatically raise pull requests whenever it detects a new version of a dependency in your configured package ecosystems.
To enable this, you add a dependabot.yml file to your repository (typically under .github/dependabot.yml). Below is a sample configuration and a breakdown of its options:
version: 2
updates:
- package-ecosystem: nuget
directories:
- /apps/app1
- /apps/app2
schedule:
interval: daily
labels:
- nuget
ignore:
- dependency-name: FluentAssertions
versions:
- ">=8.0.0"
- package-ecosystem: terraform
directory: /terraform
schedule:
interval: daily
labels:
- terraform
- package-ecosystem: github-actions
directory: /
schedule:
interval: daily
labels:
- github-actions
Let’s review the key aspects:
package-ecosystem: Specifies the type of dependencies to monitor (e.g.,nuget,npm,terraform,github-actions).directoryordirectories: The path(s) in your repo where the manifest or lock files are located. For some ecosystems, you can specify multiple directories.schedule: Controls how often Dependabot checks for updates. Common intervals aredaily,weekly, ormonthly.labels: Adds custom labels to PRs for easier filtering and triage.ignore: Lets you exclude specific dependencies or versions from automatic updates. In the example above, updates forFluentAssertionsversion 8.0.0 and above are ignored.
This configuration allows you to tailor Dependabot to your team’s workflow. For example, you might want daily updates for critical dependencies, but only weekly updates for less critical ones. You can also combine security and version updates for comprehensive coverage.
For further reading, GitHub provides a sample repo for setting up both security and version updates.
Bonus: Auto-Merge Dependabot PRs
So far, all of the PRs we’ve discussed for updating dependencies have required manual review and merging. While researching some GitHub repositories, I came across a GitHub Workflow that automatically marks non-major Dependabot update PRs as auto-merged.
name: Auto-merge dependabot updates
on:
pull_request:
branches: [ main ]
permissions:
pull-requests: write
contents: write
jobs:
dependabot-merge:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
if: ${{ github.actor == 'dependabot[bot]' }}
steps:
- name: Dependabot metadata
id: metadata
uses: dependabot/fetch-metadata@v2.4.0
with:
github-token: "${{ secrets.GITHUB_TOKEN }}"
- name: Enable auto-merge for Dependabot PRs
# Only if version bump is not a major version change
if: ${{steps.metadata.outputs.update-type != 'version-update:semver-major'}}
run: gh pr merge --auto --squash "$PR_URL"
env:
PR_URL: ${{github.event.pull_request.html_url}}
GITHUB_TOKEN: ${{secrets.GITHUB_TOKEN}}
The workflow is triggered by new PRs to main, checking that the PR has been raised by Dependabot. If raised by Dependabot, the metadata is retrieved to determine whether the package is a major change. Lastly, if not a major update, the GitHub CLI is used to set the PR to auto-merge (once all checks have passed) as well as to squash merge.
Introducing Renovate
During a recent conversation with a colleague, I was introduced to Renovate as an alternative to Dependabot. Renovate is an open-source and highly customisable automated dependency update tool.
For the purposes of this post, I’m going to focus on configuring and running Renovate in GitHub, hosted by Mend.io. However, Renovate is multi-platform, including the ability to self-host.
Recreating Dependabot in Renovate
Like GitHub’s Dependabot, Renovate also provide a great demo repo detailing:
- Installing the GitHub app
- Onboarding a repository
- Customising Renovate
- Reviewing PRs
- Interacting with the dashboard
By the end of the tutorial, you should end up with a renovate.json file similar to the one below:
{
"$schema": "https://docs.renovatebot.com/renovate-schema.json",
"extends": [
"config:base"
],
"prHourlyLimit": 3,
"packageRules": [
{
"matchUpdateTypes": ["major"],
"dependencyDashboardApproval": true
}
]
}
The renovate.json file is the equivalent of dependabot.yml and we can see that with very minimal configuration we can automate dependency updates.
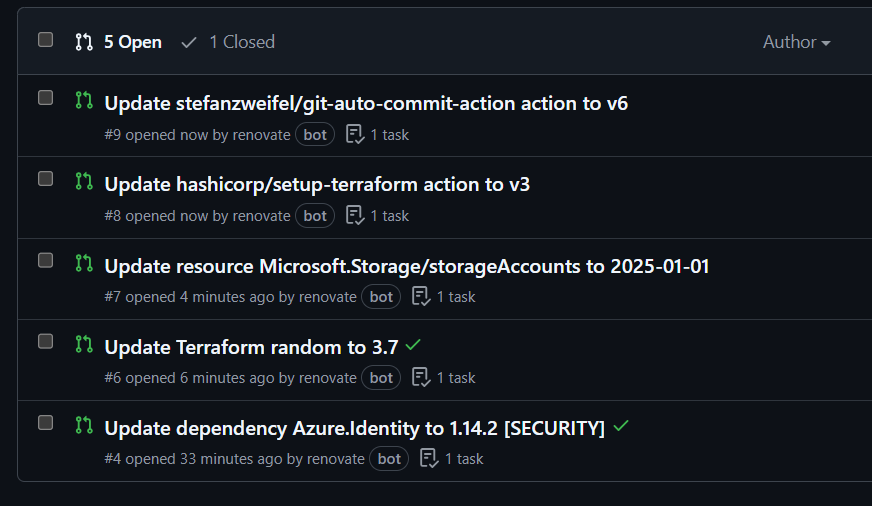
In fact, in a sample repo with the basic config supplied by the initial Renovate onboarding PR, we can see update PRs raised for my out-of-date Bicep, Terraform, GitHub Actions and NuGet dependencies.
{
"$schema": "https://docs.renovatebot.com/renovate-schema.json",
"extends": [
"config:recommended"
],
"labels": [
"dependencies",
"",
""
],
"vulnerabilityAlerts": {
"addLabels": ["security"]
},
"packageRules": [
{
"groupName": "FluentAssertions Ignore",
"matchManagers": ["nuget"],
"matchPackageNames": ["FluentAssertions"],
"allowedVersions": "<8.0.0"
}
]
}
To replicate the Dependabot configuration we discussed earlier, I expanded the default configuration as shown above.
In this configuration:
- The
config:basepresets have been replaced withconfig:recommended - Custom labels have been added using template values to categorise PRs
- Security updates are labelled with
security - The
FluentAssertionsv8 packages have been ignored
Once again, with minimal additional configuration, we’ve been able to add significant value to the dependency updates raised.
Automating Merging Updates
I covered the auto-merging of Dependabot updates as a bonus, since it’s currently not natively supported. However, with Renovate, this functionality is natively available.
{
"$schema": "https://docs.renovatebot.com/renovate-schema.json",
"extends": [
"config:recommended",
":automergeMinor",
"security:openssf-scorecard"
],
"labels": [
"dependencies",
"",
""
],
"automergeStrategy": "squash",
"minimumReleaseAge": "14 days",
"separateMajorMinor": true,
"vulnerabilityAlerts": {
"addLabels": ["security"]
},
"packageRules": [
{
"groupName": "Alternate Release Age",
"matchPackageNames": ["some-fast-package"],
"minimumReleaseAge": "2 days"
}
]
}
Expanding on the Renovate configuration covered in the previous section, I’ve added a few extra settings:
:automergeMinorhas been enabled to allow minor and patch updates to be auto-merged (once all checks pass)automergeStrategyhas been set to squash as this is my preferred merge styleminimumReleaseAgeadds a check that an update is at least 14 days old as recommended by RenovateseparateMajorMinorhas been enabled to ensure separate PRs are raised for major and minor updates- A custom
packageRulehas been added to override the defaultminimumReleaseAgefor fast updating packages - Lastly, the
security:openssf-scorecardpreset has been added to include the OpenSSF scoring for a package to indicate the security posture of the updated package.
Let’s look at a sample PR using this revised configuration.
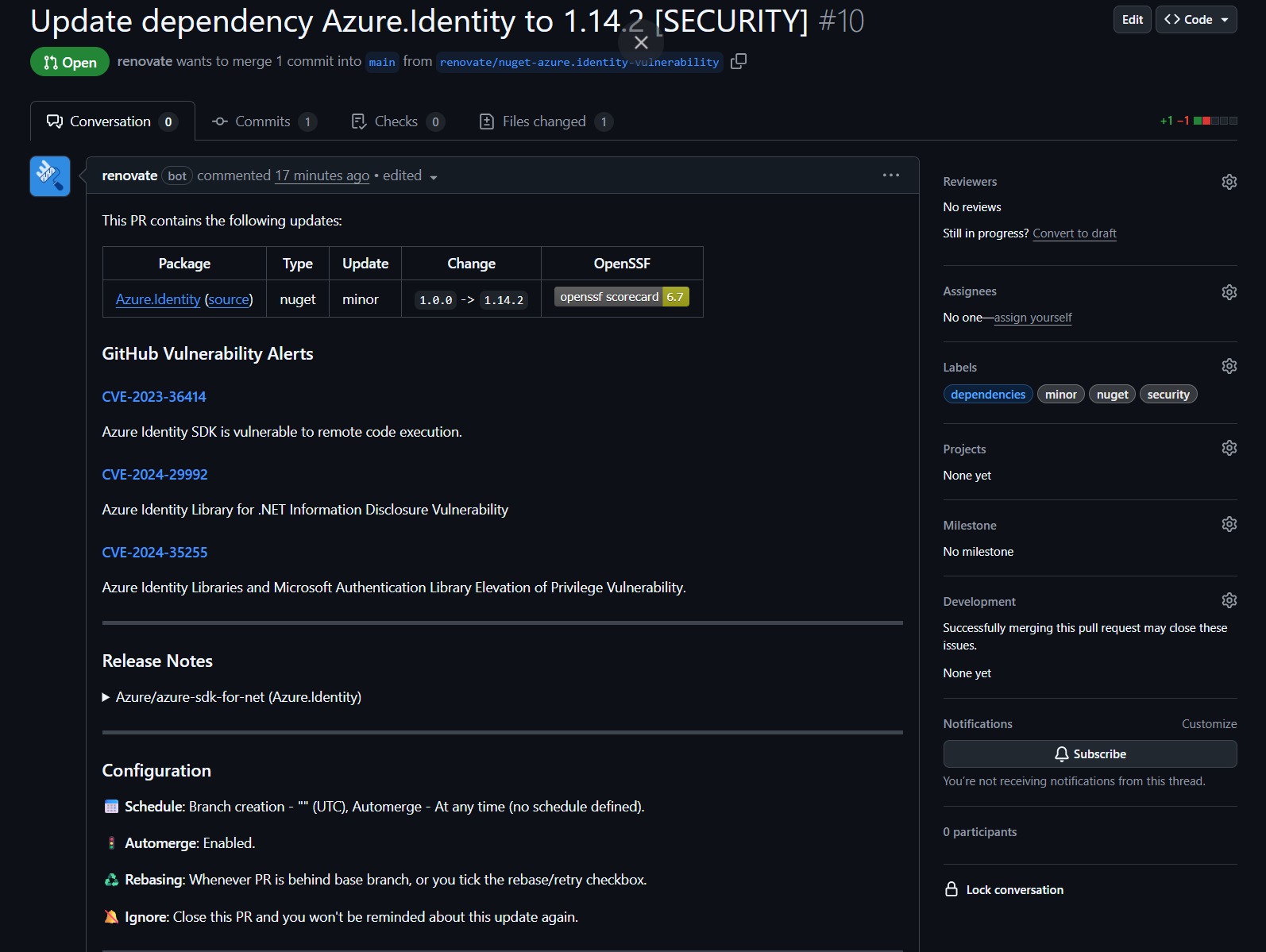
Using the same Azure.Identity dependency as an example, we can see a lot of the details Dependabot included, with the addition of the OpenSSF score, a list of CVEs being addressed (in the case of security updates) and labels categorising the PR. In the Configuration section, we can also see that Automerge is enabled as the update is classed as minor.
Wrapping Up
Automating dependency updates, especially when combined with automated checks and CI pipelines, can significantly accelerate development and improve security and is an essential part of modern software development. By staying on top of updates, teams ensure that bug fixes and security patches are applied promptly, reducing manual effort and allowing developers to focus on building new features rather than maintenance.
Dependabot is a great tool for getting started with automated updates, thanks to its seamless integration with GitHub and straightforward configuration. It provides robust support for security and version updates, making it ideal for teams already using GitHub as their source code platform.
For those seeking more flexibility, Renovate is a highly customisable alternative with support for multiple platforms, including self-hosting options. Renovate offers advanced configuration, powerful grouping and scheduling features, and native support for auto-merging updates, making it suitable for complex or multi-repository environments.
By leveraging these tools, you can keep your dependencies up-to-date, improve your project’s security posture, and free up developer time for innovation and delivery.

Comments